Effect of vulcanization on rubber grommets
Most rubber grommets are used after vulcanization. After vulcanization, the rubber not only forms a bulk network structure, but also changes the chemical composition of the rubber. The oxidative behavior of the rubber is affected by the cross-linking bonds, the extra-network substances formed by the mutual reaction of the complexing agents, and the mutated structure formed by vulcanization.
The effect of the key type
Oxidation tests on carbon black natural rubber which were vulcanized separately by conventional, effective and peroxide vulcanization systems showed that the oxidation rate was decreased in the order of conventional > effective > peroxide.
For atmospheric oxidation tests in loot, they absorb oxygen from the atmosphere for 0.5% (mass fraction) at 27h, 53h and 118h, respectively. The experimental curve further proves this feature, which indicates that the cross-linking bond, especially the polysulfide bond, is susceptible to oxidation. The oxygen absorption rate of the vulcanized rubber is related to the dissociation energy of the cross-linking bond, and the dissociation energy is not easily oxidized.
Compared with monosulfide bonds, disulfide bonds and carbon-carbon bonds, polysulfide bonds are easily cleavable into free radicals to cause oxidation of rubber due to the lowest dissociation energy. The experimental curves shown in the figure show that the more polysulfide bonds contained in the vulcanized rubber, the less resistant to oxidation. The polysulfide bond is the most crosslinkable bond in the vulcanizate of the ordinary vulcanization system.
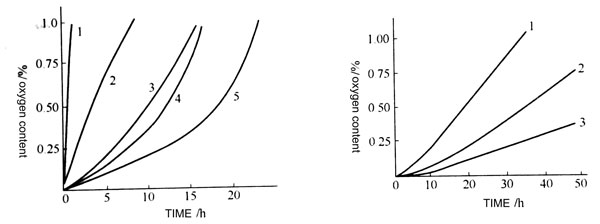
Oxygen absorption curves of different vulcanization systems
The role of TMTD in vulcanization
Effects of extra-network materials in vulcanized rubber Natural rubber vulcanized with TMTD has good oxidation resistance. If zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate formed during the vulcanization period is extracted with acetone before oxidation, the oxidation resistance of the vulcanizate is no longer superior to that of a general sulfur accelerator vulcanized rubber. This indicates that the excellent oxidation resistance of TMTD vulcanizate is neither contributed by cross-linking characteristics nor molecular pendant group characteristics, but contributed by the extra-network material zinc dimethyldithiocarbamate.
Influence of the mutated structure in the vulcanizate During the vulcanization process, the resulting intramolecular sulfur ring, promoter/sulfur pendant group, conjugated triene and other variant structures also have an effect on the oxidation of the rubber. Among them, the intramolecular sulfur ring has an effect of inhibiting oxidation, and the promoter side group and the conjugated diene can accelerate the oxidation rubber grommets.